The Scottish Government has approved Covid vaccines for five to 11-year-olds, following new advice from the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI).
So, what are Scottish Government plans to vaccinate primary pupils?
What are the benefits or risks of doing so?
And are other countries already vaccinating this age group?
We’re answering all your questions on vaccinating five to 11-year-olds.
Which children can currently get the Covid vaccine?
Before the latest announcement, all children aged 12 to 17 could already get the coronavirus vaccine.
Children in this age group can now get their second dose, as long as at least eight weeks have passed since their first dose and they haven’t had Covid in the last four weeks.
Also getting the vaccine are five to 11-year-olds at clinical risk, whose health conditions heighten the chance of them catching severe Covid.
What are the plans to vaccinate all under-12s?
On February 16, the Scottish Government announced the vaccine would be made available to all five to 11-year olds.
This follows advice from the JCVI, which recommends the universal vaccination of this age group.
However, it is currently uncertain how the rollout of this will work.
Five to 11-year-olds who are clinically vulnerable or who are a household contact of someone who is immunosuppressed are being offered two doses of the Pfizer vaccine.
The doses should be administered eight weeks apart and at least four weeks after any infection with Covid-19.
It is thought this guidance will be same for all five to 11-year-olds.
What are the benefits of vaccinating children?
According to a University of Fribourg study in Switzerland, one of the key arguments for vaccinating healthy children against Covid-19 is to protect them from long-term health consequences catching the virus could pose.
Other wider considerations include population-level factors such as reducing community transmission, vaccine supply and cost.

The avoidance of quarantine, school closures, education disruptions and other lockdown measures are also considered in whether to vaccinate children.
Reducing community transmission within schools can also help towards preventing new variants emerging and spreading through the wider population.
Are there any risks over vaccinating this age group?
Children are likely to have similar side effects to adults following the vaccine. These include pain at the injection site, and feeling more tired than usual.
Headaches, achy muscles or joints, and even fever and chills are also common. These side effects are usually temporary and typically clear up within 48 hours.
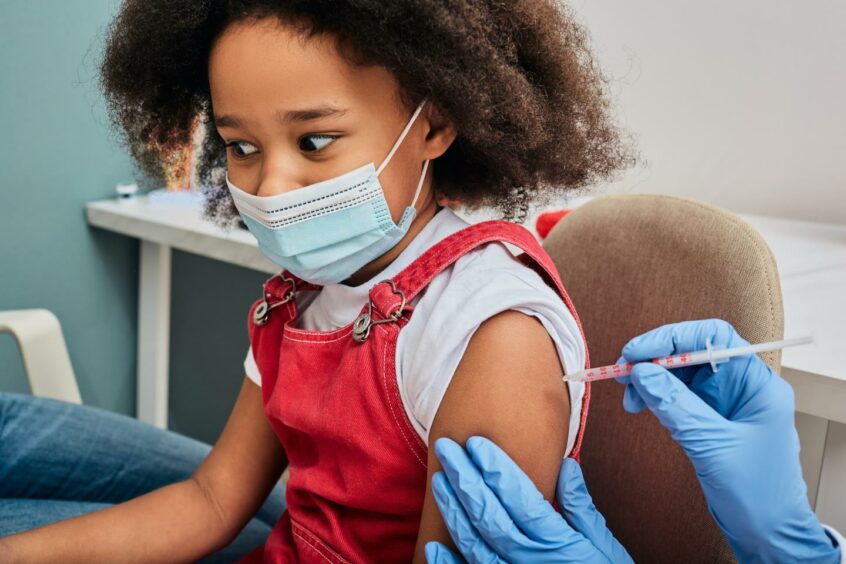

There has been some concern over whether the vaccine causes myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) and pericarditis (inflammation of the lining outside the heart).
This has, in rare cases, occurred after receiving the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines.
However, the risk is still extremely low and is a much more common complication of having Covid-19 than from getting vaccinated.
Are other countries vaccinating under-12s?
Yes. Wales and England will also offer five to 11-year-olds the vaccine, with the former saying they will deliver a “low dose”.
In Europe, countries such as Germany, Spain, Greece and Hungary are among those vaccinating this age group.
The EU regulator has given approval for primary school-age children to receive the Pfizer vaccine.
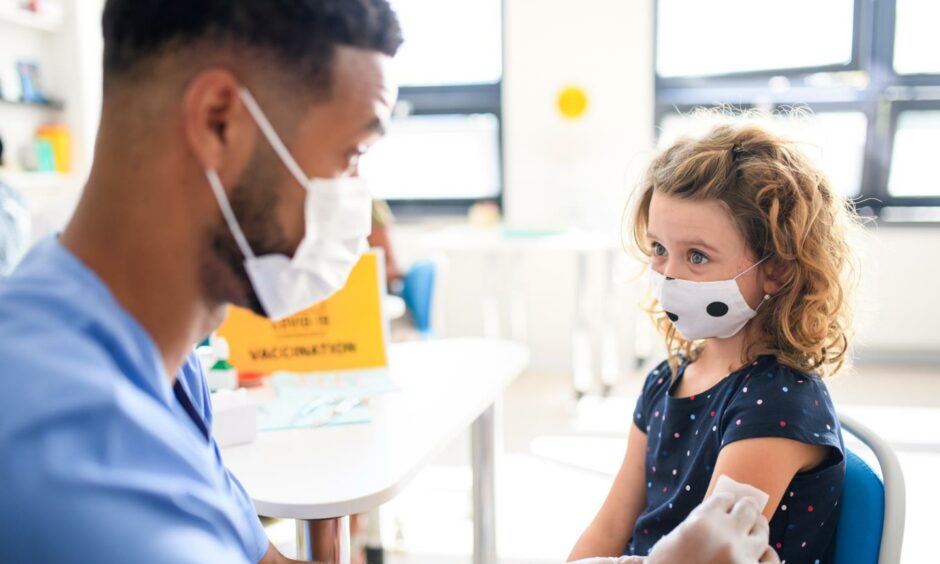

Further afield, Pfizer has also been approved for five to 11-year-olds in Australia, and the US.
The Sinovac vaccine (which has not been approved for use in the UK) has been approved for children as young as three in China and Hong Kong, and six in Indonesia.