Thyroid disease is when the thyroid gland fails to make the right amount of hormones for your body. It is extremely common with one in 20 people in the UK experiencing symptoms.
For some people this may mean little or no medical intervention, while for others it can lead to life-threatening conditions such as cancer or heart disease.
But what are the symptoms of thyroid problems, both overactive and underactive, and what treatment is available?
We’re answering your questions for World Thyroid Day.
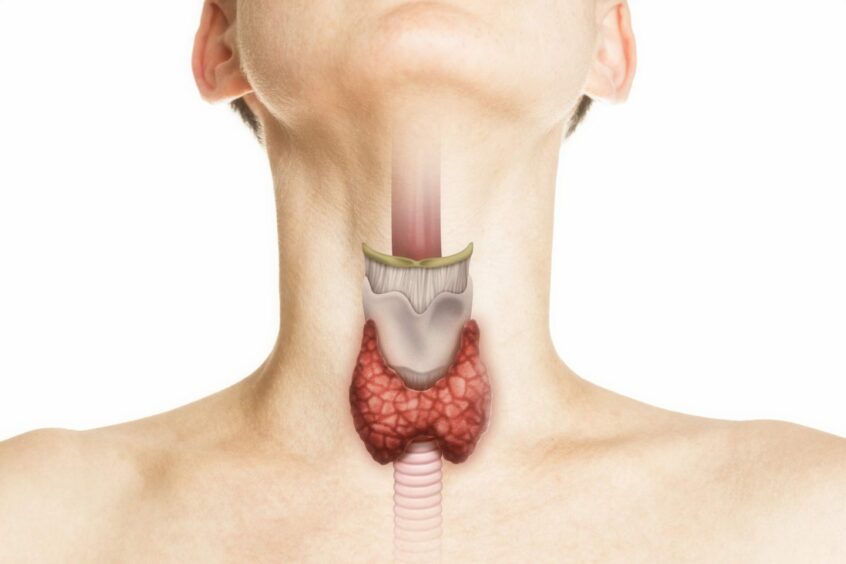
What is the thyroid?
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, just in front of the windpipe. It produces hormones that affect heart rate, body temperature and metabolism.
Having too much – or too little – of these hormones can cause unpleasant and potentially serious problems that may need treatment.
Too little thyroid hormone is known as hypothyroidism or underactive thyroid. Too much is classed as being hyperthyroid or overactive.
Thyroid problem symptoms
Basic symptoms of being hyperthyroid (having too much thyroid hormone) include:
- nervousness, anxiety and irritability
- difficulty sleeping
- persistent tiredness and weakness
- warm skin or excessive sweating
- swelling in your neck
- irregular or unusually fast heart rate
- weight loss.
Hypothyroid (having too little thyroid hormone) symptoms include:
- tiredness
- being sensitive to cold
- weight gain
- constipation
- depression
- loss of sex drive
- abnormal periods.
Other thyroid issues
Outside of thyroid imbalances, other conditions like thyroid cancer and Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis can occur.
Hashimoto’s is when the immune system attacks the thyroid. It can cause swelling in the gland and a decrease in thyroid function.
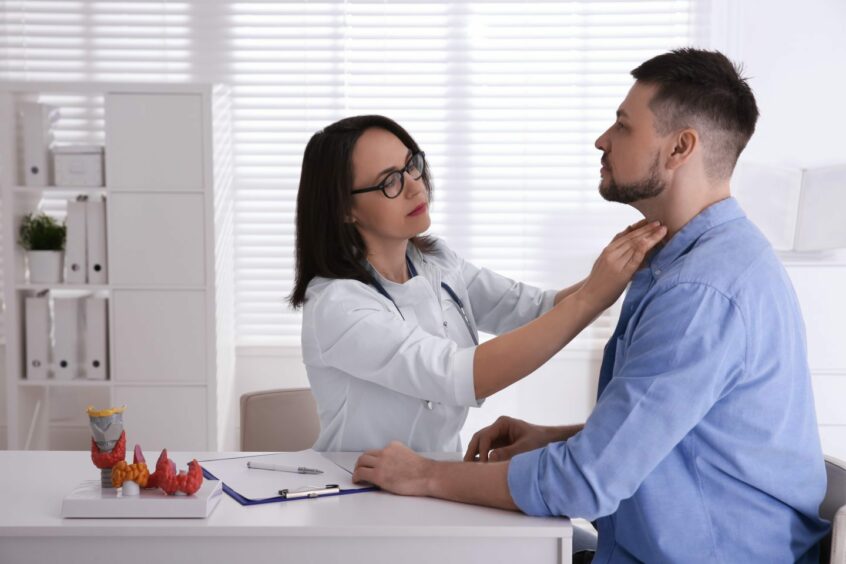

Thyroid cancers come in various forms but all involve cell changes in the body potentially affecting thyroid production.
It can often be symptomless, but the main signs include a neck lump, difficulty swallowing, swollen neck glands and a sore throat that does not improve.
Most thyroid cancers are highly treatable but some are more aggressive.
What help is available?
Hypothyroidism is mostly treated by taking daily hormone replacement tablets called levothyroxine.
Once you’re taking the correct dose, you’ll usually have a blood test once a year to monitor your hormone levels.
For hyperthyroidism, the main treatments options are medicine, radioactive iodine treatment and surgery.
Medicines called thionamides are commonly used to treat an overactive thyroid. They stop your it from producing excess hormones.
Radioactive iodine treatment is used to destroy the cells in the thyroid gland, reducing the amount of hormones it can produce.
It’s a highly effective treatment that can cure an overactive thyroid.
You’re given a drink or capsule that contains iodine and a low dose of radiation, which is absorbed by your thyroid.

Occasionally, surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid is the recommended treatment option.
Usually, the whole gland is removed, because this stops the symptoms of hyperthyroidism coming back.
In this case, you’ll need to take medicine for the rest of your life to make up for not having a thyroid gland. These are the same medicines that are used to treat hypothyroidism.
For people who have thyroid cancer, surgery or radioactive iodine treatment may be offered.
For more information on causes and treatments visit thyroiduk.org











Conversation